Type of Pain
WHAT IS PAIN?
Pain is a viscious enemy of a normal human life. Every person has experienced some kind of physiological pain, minor or severe, at WHO has recognised this pain, very aptly, as a kind of disease.
Pain is an uncomfortable feeling that tells you something may be wrong. It can be steady, throbbing, stabbing, aching, pinching, or described in many other ways. Sometimes, it’s just a nuisance, like a mild headache. Other times it can be debilitating. Pain can bring about other physical symptoms, like nausea, dizziness, weakness or drowsiness. It can cause emotional effects like anger, depression, mood swings or irritability. Perhaps most significantly, it can change your lifestyle and impact your job, relationships and independence.
Pain is classified as either acute or chronic. Acute pain is usually severe and short-lived, and is often a signal that your body has been injured. Chronic pain can range from mild to severe, is present for long periods of time, and is often the result of a disease that may require ongoing treatment. Pain affects other organs of the body as well, affecting regular routine of life as well a psychological and social aspects of it.
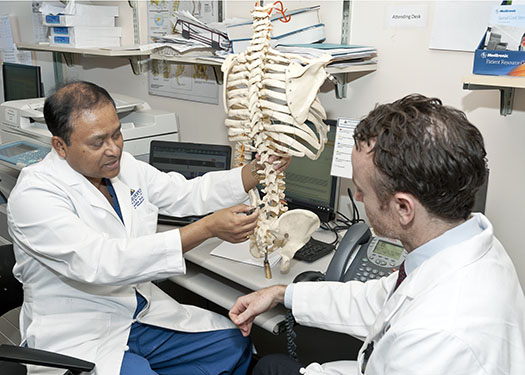
1) SPINAL PAIN

Pain is a viscious enemy of a normal human life. Every person has experienced some kind of physiological pain, minor or severe, at WHO has recognised this pain, very aptly, as a kind of disease.
Pain is an uncomfortable feeling that tells you something may be wrong. It can be steady, throbbing, stabbing, aching, pinching, or described in many other ways. Sometimes, it’s just a nuisance, like a mild headache. Other times it can be debilitating. Pain can bring about other physical symptoms, like nausea, dizziness, weakness or drowsiness. It can cause emotional effects like anger, depression, mood swings or irritability. Perhaps most significantly, it can change your lifestyle and impact your job, relationships and independence.
Pain is classified as either acute or chronic. Acute pain is usually severe and short-lived, and is often a signal that your body has been injured. Chronic pain can range from mild to severe, is present for long periods of time, and is often the result of a disease that may require ongoing treatment. Pain affects other organs of the body as well, affecting regular routine of life as well a psychological and social aspects of it.
2) BACK PAIN
Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like your mid or upper back, a hernia in the groin, or a problem in the testicles or ovaries.
You may feel a variety of symptoms if you’ve hurt your back. You may have a tingling or burning sensation, a dull aching, or sharp pain. You also may experience weakness in your legs or feet.
It won’t necessarily be one event that actually causes your pain. You may have been doing many things improperly — like standing, sitting, or lifting — for a long time. Then suddenly, one simple movement, like reaching for something in the shower or bending from your waist, leads to the feeling of pain.
3) NECK PAIN
Neck pain may begin in any of the structures in the neck. These include muscles and nerves as well as spinal vertebrae and the cushioning disks in between. Neck pain may also come from regions near the neck, like the shoulder, jaw, head, and upper arms. We will limit our discussion about neck pain of spine origin.
When your neck is sore, you may have difficulty moving it, especially to one side. Many people describe this as having a stiff neck. If neck pain involves nerves (for example, significant muscle spasm pinching on a nerve or a slipped disk pressing on a nerve), you may feel numbness, tingling, or weakness in your arm, hand, or elsewhere.
A common cause of neck pain is muscle strain or tension. Usually, everyday activities are to blame. Such activities include bending over a desk for hours, having poor posture while watching TV or reading, placing your computer monitor too high or too low, sleeping in an uncomfortable position, or twisting and turning the neck in a jarring manner while exercising.
4) INTERVERTEBRAL DISCS
The intervertebral discs make up one fourth of the spinal column’s length. There are no discs between the Atlas (C1), Axis (C2), and Coccyx. Discs are not vascular and therefore depend on the end plates to diffuse needed nutrients. The cartilaginous layers of the end plates anchor the discs in place.
The intervertebral discs are fibrocartilaginous cushions serving as the spine’s shock absorbing system, which protect the vertebrae, brain, and other structures (i.e. nerves). The discs allow some vertebral motion: extension and flexion. Individual disc movement is very limited – however considerable motion is possible when several discs combine forces.
The annulus fibrosus is a strong radial tire–like structure made up of lamellae; concentric sheets of collagen fibers connected to the vertebral end plates. The sheets are orientated at various angles. The annulus fibrosus encloses the nucleus pulposus. Although both the annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus are composed of water, collagen, and proteoglycans (PGs), the amount of fluid (water and PGs) is greatest in the nucleus pulposus. PG molecules are important because they attract and retain water
5) SLIPPED DISC OR DISC PROLAPSE

The inter-vertebral discs are protective cushion-like shock-absorbing pads between the two bones of the spine called vertebrae. These discs are soft gel filled pads bounded by few layers of membrane called lamella.
These discs do not actually “slip,” they may split or rupture. Following this rupture, the gel escape into the surrounding tissue. The leaking jellylike substance can produce pressure on the spinal cord or on a single nerve root and cause pain either around the damaged disc or anywhere along the area controlled by that nerve. This condition is also known as a herniated disc, ruptured disc, prolapsed disc, or, more commonly, slipped disc.
The most frequently affected area is the low back, but any disc can rupture, including those in the neck. When the discs of low back are ruptured there will be pain in low back that will radiate to the legs. Similarly in case of neck there will be pain in neck that will be radiating to the hands.
The nature of the pain is frequently electric shock-like pain or burning pain. This pain may be associated with some numbness, tingling sensations and sometime some muscle weakness. As there are so many discs in the spine, the exact area of pain depends on the nerve root involved and that again depends on the disc that is involved.
6) FACET JOINT
A joint is where two or more bones are joined. Joints allow motion (articulation). The joints in the spine are commonly called Facet Joints. Other names for these joints are Zygapophyseal or Apophyseal Joints.
Each vertebra has two sets of facet joints. One pair faces upward (superior articular facet) and one downward (inferior articular facet). There is one joint on each side (right and left). Facet joints are hinge–like and link vertebrae together. They are located at the back of the spine (posterior).
Facet joints are synovial joints. This means each joint is surrounded by a capsule of connective tissue and produces a fluid to nourish and lubricate the joint. The joint surfaces are coated with cartilage allowing joints to move or glide smoothly (articulate) against each other.
7) KNEE PAIN
A decent result can be achieved in patients of knee pain due to wear and tear with the help of Ozone Therapy and Prolo Therapy.
The knee is a joint that has three compartments. The thigh bone (femur) meets the large shin bone (tibia) forming the main knee joint. This joint has an inner (medial) and an outer (lateral) compartment. The kneecap (patella) joins the femur to form a third compartment, called the patellofemoral joint.
The knee joint is surrounded by a joint capsule with ligaments strapping the inside and outside of the joint (collateral ligaments) as well as crossing within the joint (cruciate ligaments). These ligaments provide stability and strength to the knee joint. The meniscus is a thickened cartilage pad between the two joints formed by the femur and tibia. The meniscus acts as a smooth surface for motion and absorbs the load of the body above the knee when standing.
8) SPASTICITY

Spasticity is a disease caused by a disease of, or an injury to, brain and vertebral column. It can occur in children after Cerebral Plasy, Head Injury and Brain Stroke.Major symptoms of Spasticity are hardness in muscles and joint lock.
Children with cerebral palsy tend to exhibit one of the following spasticity patterns:
1) Diplegic pattern: Scissoring, crouching, and toe walking
2) Quadriplegic pattern: Diplegic patterning in addition to flexion of the elbow, flexion of the wrist and fingers, adduction of the thumb, and internal rotation, pronation, or adduction of the arms
3) Hemiplegic pattern: Plantar flexion of the ankle, flexion of the knee, adduction of the hip, flexion of the wrist and finger, adduction of the thumb, and flexion, internal rotation, pronation, or adduction of the arms
Children with cerebral palsy tend to exhibit one of the following spasticity patterns:
1) Diplegic pattern: Scissoring, crouching, and toe walking
2) Quadriplegic pattern: Diplegic patterning in addition to flexion of the elbow, flexion of the wrist and fingers, adduction of the thumb, and internal rotation, pronation, or adduction of the arms
3) Hemiplegic pattern: Plantar flexion of the ankle, flexion of the knee, adduction of the hip, flexion of the wrist and finger, adduction of the thumb, and flexion, internal rotation, pronation, or adduction of the arms
9) MIGRAINE AND HEADACHE
Many a times, a single particular cause for the headache cannot be diagnosed. Even after multiple CT Scans or MRI, the cause for such headache cannot be diagnosed and usually such headache is treated as a case of Migraine.
Nearly 10 million people in the India have migraines, and three times as many women as men have them. Migraines are pulsating headaches, often on one side of the head. Physical activity may intensify the pain, but symptoms can vary from person to person and from one attack to the next.
“In patients who have migraines, we’re going to treat all of their headaches as potential migraines.”
– Dr. jayesh Thakrar, MD, partner and cofounder of the Advanced Pain care clinic,surat,Gujarat,India.
10) POST SURGICAL PAIN
Epidural Fibrosis is a condition which may arise after Spinal Cord operation, which is a natural process. This can lead to a normal or a different kind of pain.
The epidural catheter can be left in place for several days if needed to control postoperative pain. A continuous infusion of pain relievers, including numbing medications (local anesthetics) or opioid medications, can be delivered through the catheter to control pain.
Patient-controlled epidural analgesia (PCEA), similar to PCA, enables you to give yourself an extra dose of the pain medication by pushing a button. It, too, has built-in safeguards so that you don’t give yourself too much medication.
11) CANCER PAIN
No definite treatment is available for cancer in advanced stages and Recurrent cancer. Such cancer can spread to the different parts of the body, making the remaining life of the patient merciful. With the help of pain management techniques such patients can be provided relief.
In most cases, prostate cancer symptoms are not apparent in the early stages of the disease. The symptoms of prostate cancer may be different for each man and any one of these symptoms may be caused by other conditions. As a result, routine screenings in the form of digital rectal exams (DRE) and prostate specific androgen (PSA) tests are important.
12) PAIN IN DIABETES
Damage to the outer coat of main veins in legs due to an old condition of Diabetis can cause inflammation and continous pain. An effective treatment can be provided through Lumbar Sympathic System Block.
Diabetes can lead to a variety of complications. Leg pain and cramps often occur as a result of a form of nerve damage called diabetic neuropathy. If diabetes damages nerves in your arms or legs, it’s referred to as diabetic peripheral neuropathy. This condition can be a direct result of long-term high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) in type 2 diabetes.
Besides pain, tingling and numbness are also common in this condition. Peripheral neuropathy can result in serious foot and leg conditions. Catching nerve damage early is important in preventing these issues, which can eventually require lower leg amputations.
If you’re experiencing leg pain and cramps related to diabetes, you have options for alleviating painful symptoms. Taking control of diabetic leg pain and cramps will also help to prevent serious injury and improve your quality of life.
13) FROZEN SHOULDER
The patients of Frozen Shoulder can be treated with Supra Scapular Nerve Block which makes them pain free and provides movement immediately.
Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis, is a condition characterized by stiffness and pain in your shoulder joint. Signs and symptoms typically begin gradually, worsen over time and then resolve, usually within one to three years.
Your risk of developing frozen shoulder increases if you’re recovering from a medical condition or procedure that prevents you from moving your arm — such as a stroke or a mastectomy.
Treatment for frozen shoulder involves range-of-motion exercises and, sometimes, corticosteroids and numbing medications injected into the joint capsule. In a small percentage of cases, arthroscopic surgery may be indicated to loosen the joint capsule so that it can move more freely.
It’s unusual for frozen shoulder to recur in the same shoulder, but some people can develop it in the opposite shoulder.
14) PAIN IN VASCULAR INSUFFICIENCY
Blood circulation can be improved in patients of Vascular Insufficiency with the help of Sympathetic System Block which provides relief in pain.
Normally, valves in your deeper leg veins keep blood moving forward toward the heart. With chronic venous insufficiency, vein walls are weakened and valves are damaged. This causes the veins to stay filled with blood, especially when you are standing. Chronic venous insufficiency is a long-term condition. It occurs because a vein is partly blocked, or blood is leaking around the valves of the veins.
15) TRIGEMINAL NEURALGIA
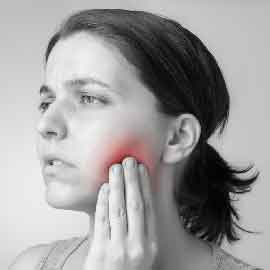
Trigeminal Neuralgia has been described as one of the most severe pain syndromes. It is characterized by excruciating, electric shock like, shooting/stabbing pain in the distribution of Trigeminal nerve in the face.
It is unilateral during any one episode, abrupt onset with pain-free intervals between attacks. Pain is triggered by some non-noxious stimuli like touching of face, chewing, swallowing or even talking. Tumors, vascular malformations, dental disease, sinusitis may cause trigeminal neuralgia, but the etiology in the majority of the cases is unknown. The condition occurs more often in the middle aged and is twice as common in females as in males. In most of the patients the pain is strictly unilateral; multiple sclerosis patients constitute the majority of the 2% patients with bilateral disease.
Trigeminal neuralgia is twice as common on the right side. Most commonly patients present with pain maximum either in maxillary or mandibular divisions.
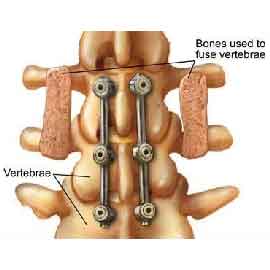
16) VERTEBROPLASTY AND KYPHOPLASTY
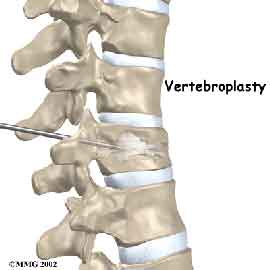
In conditions like Osteoporosis after Menopause, Tumor in Vertebral Column and Vertebral Compression Fracture, an immediate and permanent relief can be obtained with the help of pain management by Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty without any operation.
These procedures, vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty, are most commonly used in cases of severe, functionally disabling pain caused by a vertebral fracture that does not improve over a number of weeks with pain medication and treatment with brace immobilization.

